Queen Elizabeth II, whose death was announced Thursday, is often referred to as “the Queen of England” when in fact she reigned over the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth. Between the United Kingdom, Great Britain or England, confusion is frequent.
A brief summary of these different entities.
4 countries for a United Kingdom
The United Kingdom, over which Charles III now reigns, is made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Attention when we talk about Ireland, reference is made to an island, but it is made up of two very different countries that should not be confused: the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The former has Dublin as its capital and is an independent republic. As such, it remains part of the European Union, unlike its neighbor since Brexit. The second, Northern Ireland, of which Belfast is the capital, is part of the kingdom of Charles III.
When we talk about “Great Britain”, it is simply a group of England, Scotland and Wales. In short: the United Kingdom, without Northern Ireland.
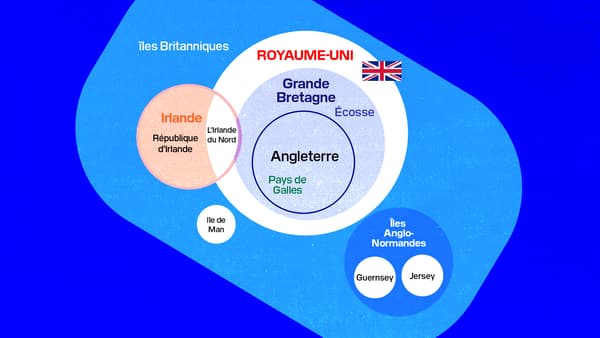
the british isles
More broadly, when speaking of the British Isles, reference is made to the entire archipelago located north of Western Europe. Or specifically: Great Britain, Ireland (or actually Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland), as well as many other small nearby islands.
These islands include three British Crown dependencies: the Isle of Man and the two Channel Islands of Jersey and Guernsey.
In particular, the United Kingdom is responsible for its defense and its international relations, without these being part of the United Kingdom or the Commonwealth.
14 overseas territories
As a former colonial empire, the UK also has 14 overseas territories, inhabited by some 300,000 people in total. These include Bermuda, the Cayman Islands, the British Virgin Islands, the Falkland Islands and Gibraltar.
Each territory has a different status, but has its own constitution and parliament, as well as its own governor.
the commonwealth
In addition to the United Kingdom, Charles III also became king of 14 other Commonwealth countries. In addition to Australia, Canada and New Zealand, there are many islands: Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Belize, Grenada, Jamaica, Papua New Guinea, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Solomon Islands. and Tuvalu.
In each of these countries, the sovereign is represented by a governor general or a viceroy who acts as head of state.
Several countries left the organization during the Queen’s reign, including Gambia, Ghana and Barbados, and it is possible that they will leave in the future. As King of New Zealand, Charles III also becomes ruler of the Cook Islands and Niue, located in the Pacific Ocean.
Source: BFM TV

